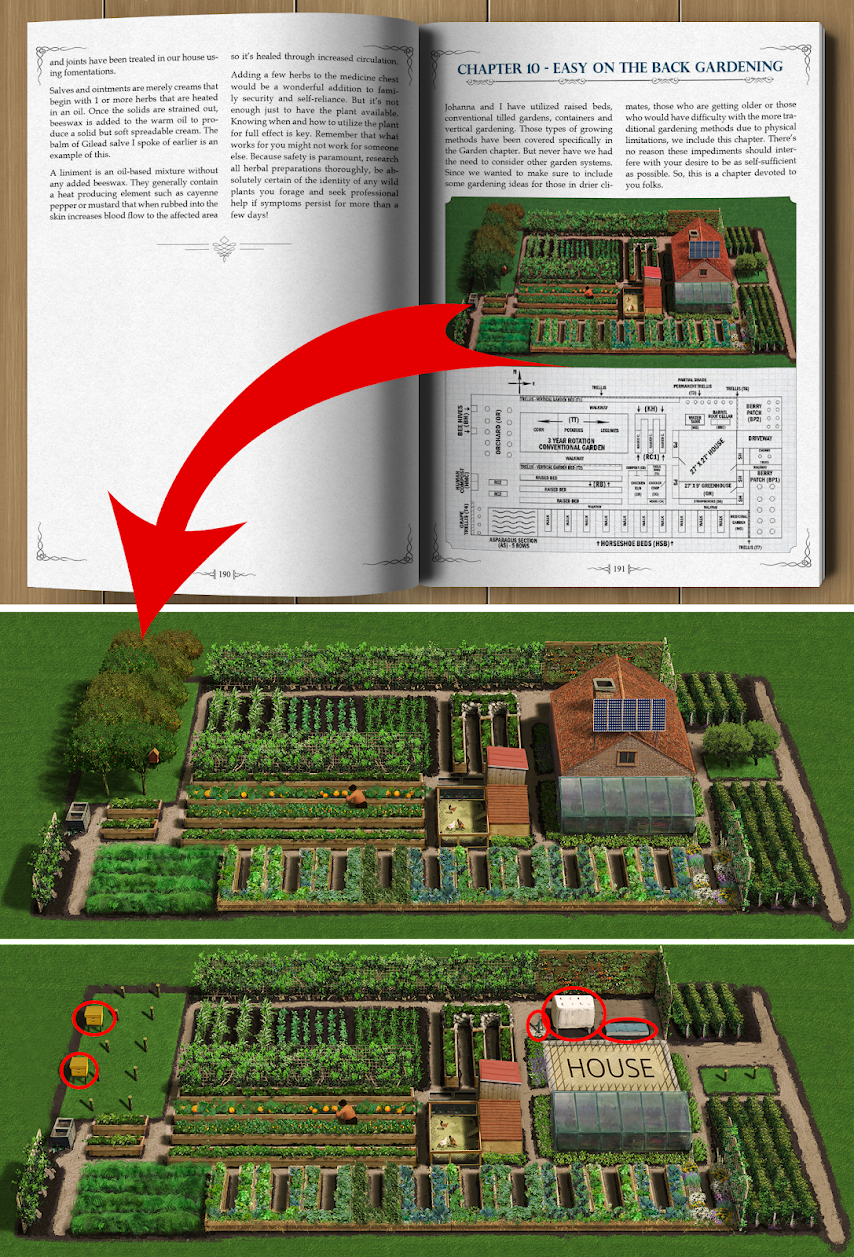
In an age where self-sufficiency and sustainability are becoming increasingly important, many people are turning their attention to their own backyards. Creating a self-sufficient backyard not only helps reduce your ecological footprint but also allows you to enjoy the fruits of your labor and connect more deeply with nature. Here are essential steps to help you transform your backyard into a self-sustaining oasis.
1. Assess Your Space and Resources
Before diving into self-sufficiency projects, take a good look at your backyard. Assess the available space, sunlight, and soil quality. Understand the local climate and how it might affect your plans. Determine the resources you have at your disposal, including water sources, tools, and the time you can invest in your project. A thorough assessment will guide your decisions throughout the process.
The Only Book You Need to Become Self Sufficient on ¼ Acre >
2. Start with Sustainable Gardening
A self-sufficient backyard often begins with a well-planned garden. Choose native plants and consider companion planting to enhance soil fertility and reduce the need for pesticides. Implement organic gardening practices to promote healthy soil and minimize environmental impact. Raised beds or container gardening can also help you control the growing environment.
3. Embrace Permaculture Principles
Permaculture is a design philosophy that focuses on creating sustainable, self-sufficient systems. Apply permaculture principles to your backyard by designing for efficiency, diversity, and resilience. Incorporate features like swales, hugelkultur beds, and rainwater harvesting to maximize your garden's productivity while minimizing resource inputs.
Watch this short presentation on how to build a self-sufficient backyard:
4. Rainwater Harvesting and Irrigation
Collecting rainwater is a crucial step in creating a self-sufficient backyard. Install rain barrels or a larger cistern system to capture rainwater from your roof. This collected water can be used for irrigation, reducing your reliance on municipal water sources. Drip irrigation systems can efficiently distribute water to your garden, minimizing waste.
5. Composting and Soil Improvement
Healthy soil is the foundation of a self-sufficient garden. Start a compost pile to recycle kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials. Compost enriches your soil with essential nutrients, reduces landfill waste, and promotes microbial activity. You can also experiment with vermiculture (worm composting) to accelerate the process.
6. Incorporate Edible Landscaping
Make your backyard both beautiful and functional by incorporating edible landscaping. Plant fruit trees, berry bushes, and edible herbs throughout your garden. Edible landscaping not only provides fresh, homegrown produce but also adds aesthetic value to your outdoor space.
7. Establish a Chicken Coop
If local regulations allow, consider keeping chickens for a steady supply of fresh eggs. A chicken coop doesn't require much space, and these birds can help control pests and provide valuable fertilizer for your garden. Ensure proper care and shelter for your feathered friends to maintain a healthy and sustainable system.
8. Beekeeping for Pollination
Bees are essential for pollinating many garden crops. Consider setting up a beehive to encourage pollination and honey production. Bees also play a vital role in ecosystem health, so you're contributing to the environment while enjoying sweet rewards.
9. Renewable Energy Sources
To further reduce your environmental impact, explore renewable energy options for your backyard. Solar panels can generate electricity for lighting, water pumps, or other energy needs. Wind turbines are another possibility if your location is suitable.
10. Preserve and Store Food
One of the ultimate goals of self-sufficiency is preserving the surplus from your garden. Learn food preservation techniques like canning, drying, and fermenting to store your harvest for the off-season. A well-stocked pantry ensures that you can enjoy your homegrown produce throughout the year.
11. Continual Learning and Adaptation
Creating a self-sufficient backyard is an ongoing journey. Stay open to learning and adapting your practices. Attend workshops, read books, and connect with the local gardening community to gather knowledge and insights. Each year, experiment with new crops and techniques to refine your self-sufficiency skills.
12. Share and Connect
Self-sufficiency doesn't mean isolation. Share your experiences and excess produce with neighbors and friends. Connect with like-minded individuals through community gardening or sustainability groups. Building a network of support and knowledge-sharing can enhance your self-sufficiency journey.
The Only Book You Need to Become Self Sufficient on ¼ Acre >
13. Wildlife-Friendly Landscaping
Incorporating wildlife-friendly features into your self-sufficient backyard is not only beneficial for local ecosystems but can also improve the health of your garden. Consider planting native species that attract pollinators like butterflies and bees. Install bird feeders and birdhouses to encourage avian visitors. Create a small pond or water feature to attract frogs, toads, and other amphibians that help control insect populations.
14. Crop Rotation and Succession Planting
To maintain soil health and optimize your garden's productivity, practice crop rotation and succession planting. Crop rotation involves changing the types of crops you grow in specific areas of your garden each season to prevent soil depletion and reduce the risk of pests and diseases. Succession planting ensures a continuous harvest by planting new crops as soon as previous ones are harvested.
15. Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle
The principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle extend to your self-sufficient backyard. Reduce waste by avoiding disposable garden products and choosing durable, long-lasting materials for your projects. Reuse items like containers, pallets, and old furniture creatively in your garden. Recycle organic matter through composting and recycling programs in your community.
16. Pest Management Strategies
Rather than relying on chemical pesticides, adopt natural pest management strategies. Encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps, which help control garden pests. Use physical barriers such as row covers to protect vulnerable plants. Research companion planting techniques that deter specific pests. Maintaining a healthy garden ecosystem is the key to minimizing pest issues.
The Only Book You Need to Become Self Sufficient on ¼ Acre >
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) about Creating a Self-Sufficient Backyard
- What is a self-sufficient backyard?
A self-sufficient backyard is a garden or outdoor space designed to produce a significant portion of your food, energy, and other resources, while minimizing environmental impact and reliance on external sources.
- How do I assess if my backyard is suitable for self-sufficiency?
Start by evaluating your available space, sunlight exposure, soil quality, and local climate. Determine your water sources, available tools, and the time you can commit to your self-sufficiency project. This assessment will help you make informed decisions.
- Can I create a self-sufficient backyard in a small space?
Yes, self-sufficiency can be achieved in small spaces, such as balconies, patios, or even indoor spaces with adequate light. Vertical gardening, container gardening, and efficient space utilization are key strategies for small-space self-sufficiency.
- Do I need advanced gardening skills to create a self-sufficient backyard?
No, you don't need advanced skills, but a basic understanding of gardening principles is helpful. There are plenty of resources, books, and online communities to support beginners in their self-sufficiency journey.
- What are the essential plants to grow in a self-sufficient backyard?
Essential plants include vegetables, fruit trees, berry bushes, and herbs that thrive in your local climate. Choose a variety of crops to ensure a diverse and year-round harvest.
- Is self-sufficiency expensive to set up and maintain?
The initial setup can require an investment in tools, materials, and infrastructure like rainwater harvesting systems or compost bins. However, over time, self-sufficiency can save you money on groceries and utilities.
- How can I deal with pests in a self-sufficient backyard without using chemicals?
Natural pest control methods include attracting beneficial insects, using physical barriers like row covers, and practicing companion planting. These methods help maintain a healthy balance in your garden.
- What are the benefits of rainwater harvesting for a self-sufficient backyard?
Rainwater harvesting reduces your reliance on municipal water sources, conserves water, and provides a free and natural source of irrigation for your garden.
- How can I incorporate renewable energy into my self-sufficient backyard?
Solar panels and small wind turbines can generate electricity for lighting, water pumps, and other energy needs. Consult with a renewable energy expert to determine the best options for your location.
- Can I create a self-sufficient backyard without keeping livestock like chickens or bees?
Yes, self-sufficiency can be achieved without livestock, but they can enhance your sustainability efforts by providing eggs, honey, and natural pest control.
- What should I do with surplus produce from my self-sufficient garden?
You can preserve surplus produce through canning, drying, freezing, or fermenting to enjoy throughout the year. Additionally, consider sharing excess produce with neighbors or donating to local food banks.
- How long does it take to establish a self-sufficient backyard?
The timeline varies depending on your initial setup and the complexity of your plans. Some aspects, like growing vegetables, can yield results in a few months, while others, like fruit trees, may take several years to mature fully.
- Is self-sufficiency a sustainable lifestyle choice?
Yes, self-sufficiency promotes sustainability by reducing your environmental impact, promoting local food production, and fostering a deeper connection with nature.
The Only Book You Need to Become Self Sufficient on ¼ Acre >